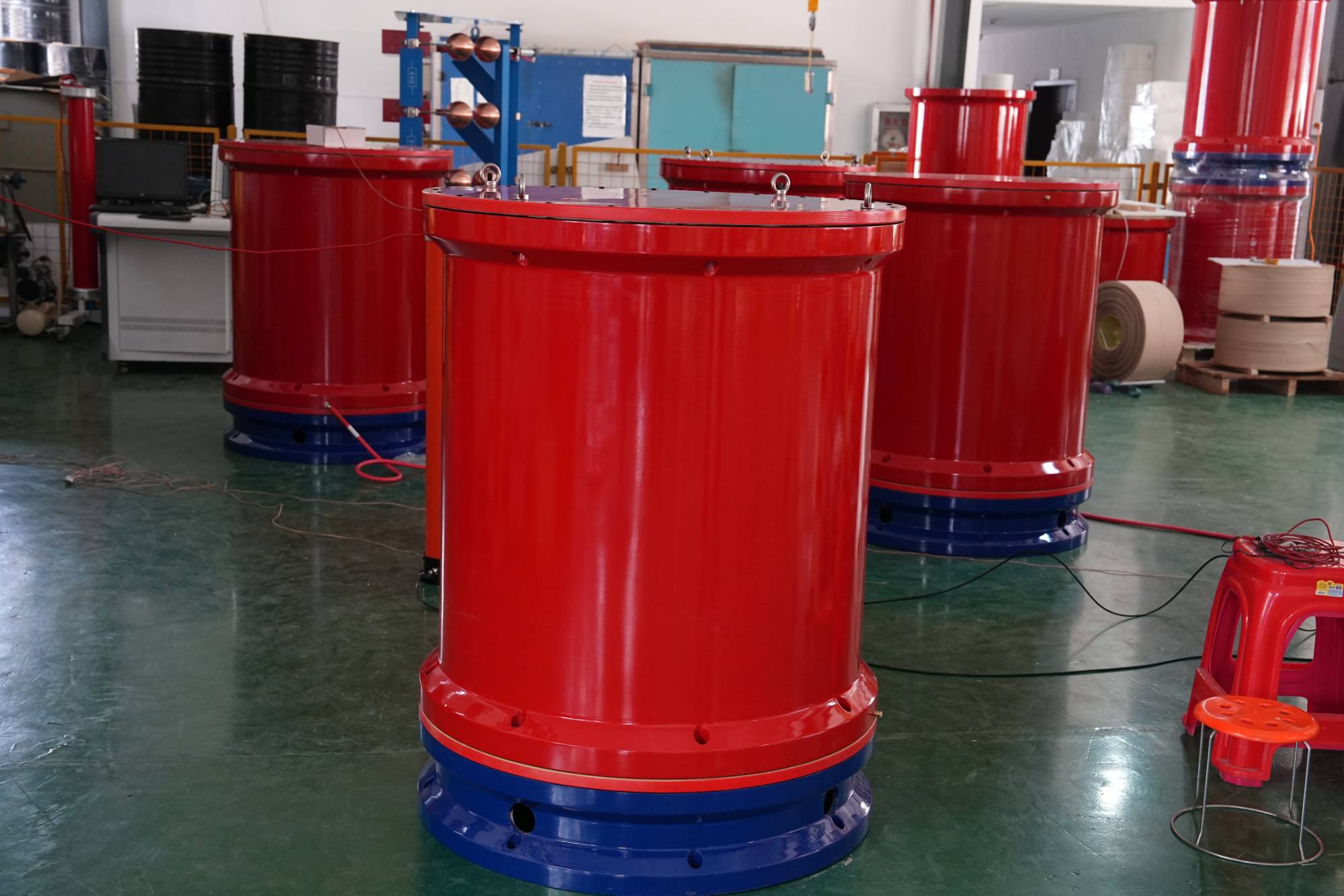
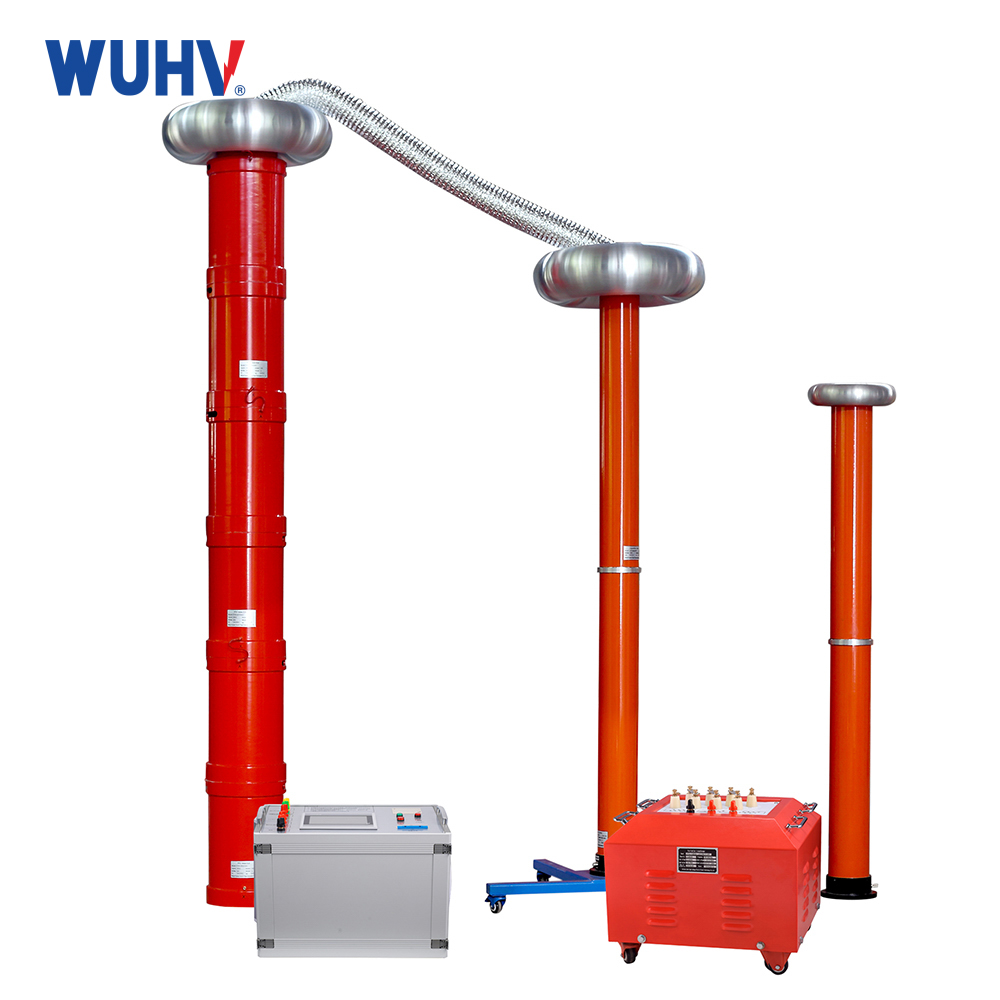
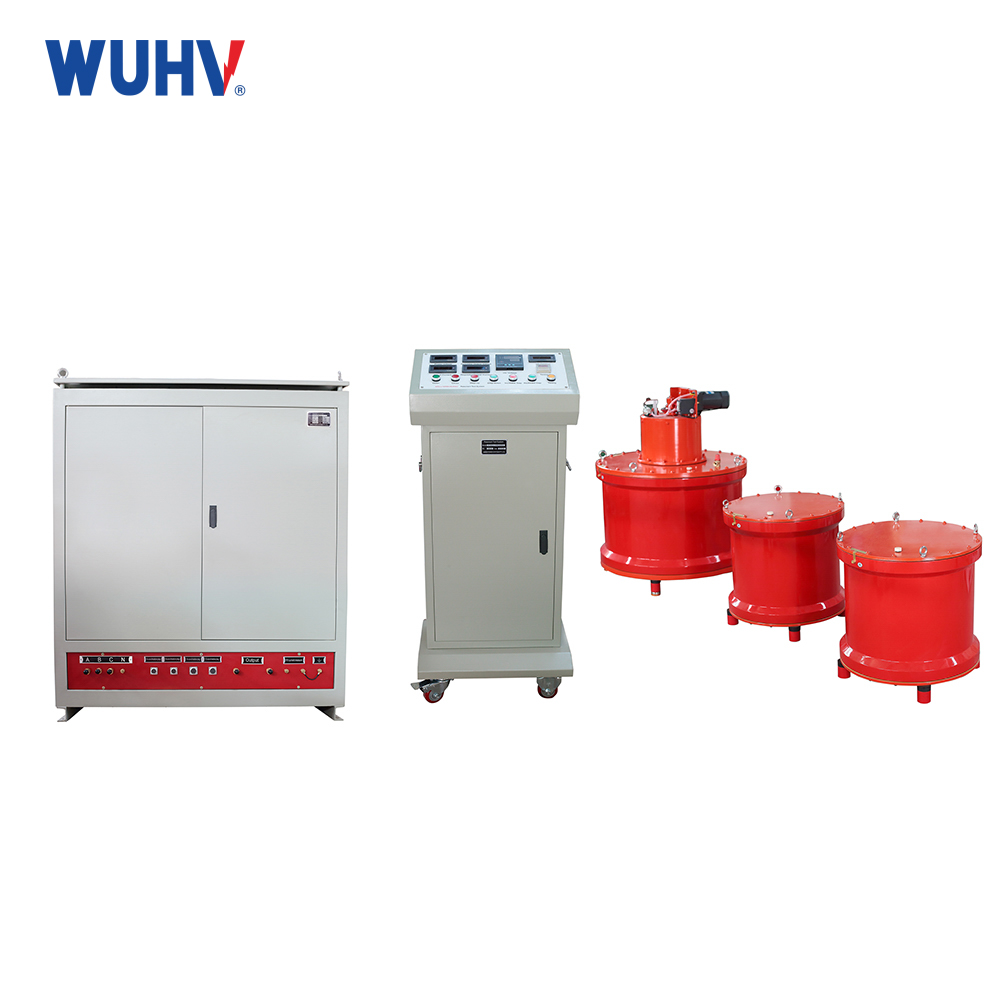
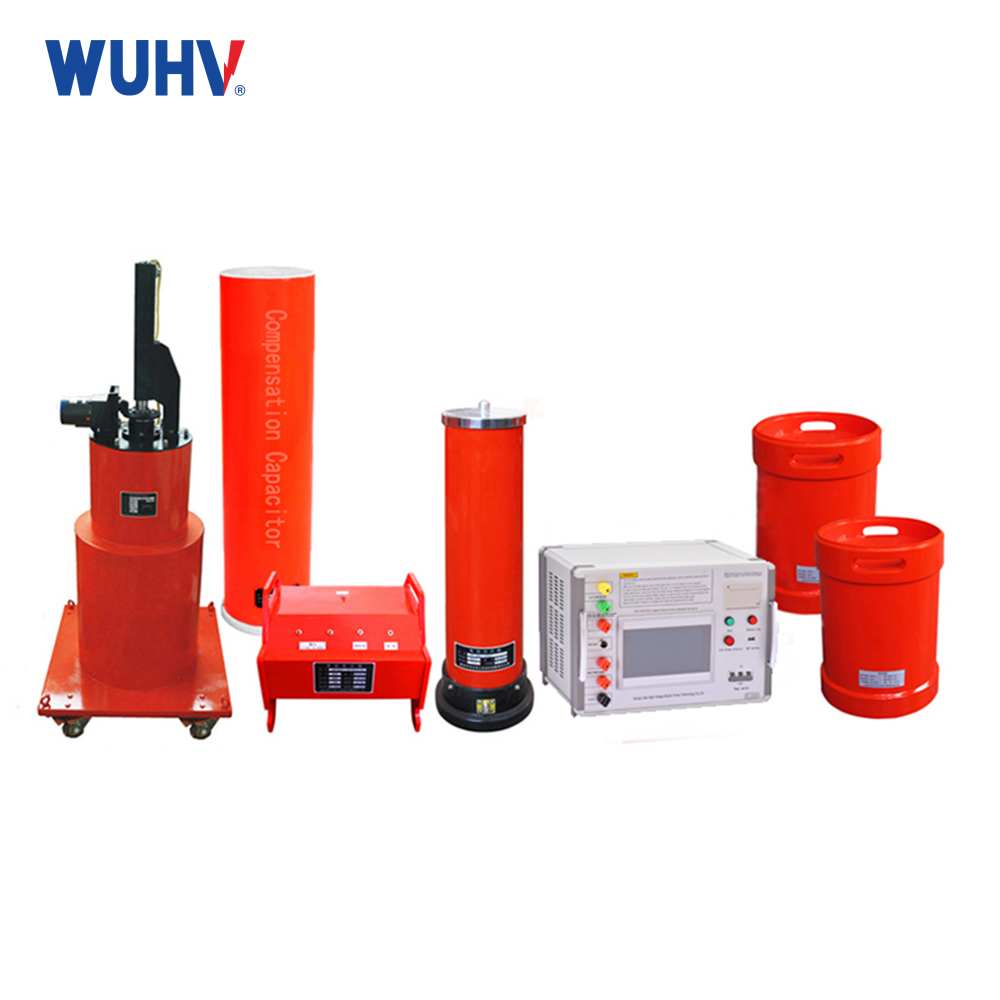
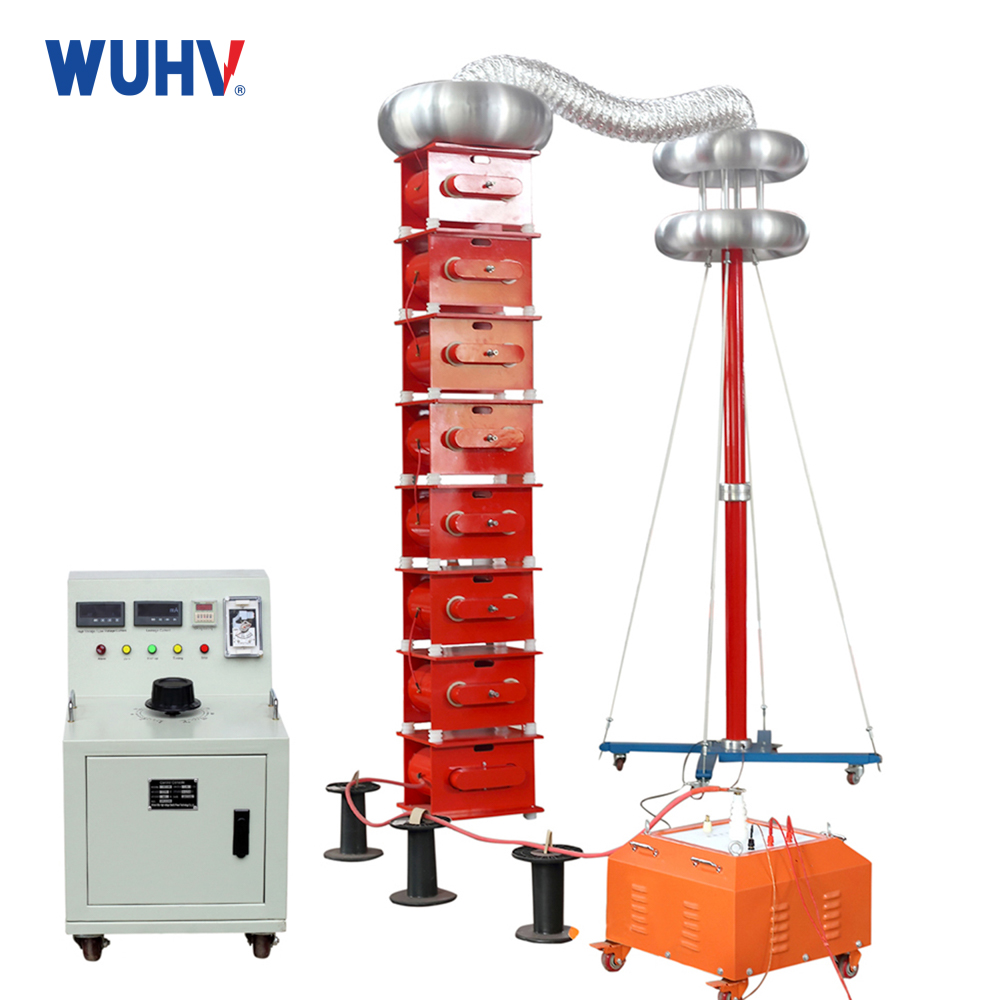
1、 Definition of Reactor
The main components of an electrical circuit are resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Inductance has the function of suppressing current changes and shifting the phase of alternating current. A wound type static induction device with inductive function is called a reactor.
2、 Characteristics of reactors
1. Iron core reactor
High noise, poor linearity of reactors, can cause magnetic leakage, local overheating, easy magnetic saturation, and coil burnout. The effects of system overvoltage, overcurrent, and harmonics cause a sharp decrease in the iron core's supersaturated reactance value, a decrease in the ability to suppress harmonics, and a low ability to withstand short-circuit currents. In addition to the above drawbacks, dry-type iron core reactors cannot operate outdoors.
2. Dry type air core reactor
Good linearity, no noise, strong overcurrent ability, strong heat dissipation ability, simple and sturdy mechanical structure, suitable for indoor and outdoor use, basically maintenance free. The disadvantage is that it has a large volume and significant loss.
3. Half core reactor
A half core reactor is a new type of reactor that is located between an iron core reactor and an air core reactor. By adding an iron core with an open magnetic circuit to the winding of the air core reactor, the half core reactor has the advantages of both iron core and air core reactors. Forming a brand new half core reactor, the wire diameter of the half core reactor is 20% smaller than that of the air core reactor, and the reactor loss is 25% lower. The linearity is close to a straight line, the impedance does not decrease with the increase of current, and the noise is less than 50db. It is easy to install in the cabinet and is a series reactor with good reactive power compensation.
The ideal reactor should have the following characteristics:
1. Oil free
2. No noise
3. Small size
4. Good linearity
5. No leakage magnetic field
6. Strong overcurrent capability
The upcoming development direction is dry-type half core magnetic shielding reactors.
3、 Function of Reactor
1. The capacitance effect on lightly unloaded or lightly loaded lines to reduce transient overvoltage at power frequency;
2. Improve voltage distribution on long-distance transmission lines;
3. To balance the reactive power in the line as much as possible under light load, prevent unreasonable flow of reactive power, and also reduce power loss on the line;
4. Reduce the steady-state power frequency voltage on the high-voltage bus when the large unit is parallel to the system, in order to facilitate synchronous parallel operation of the generator;
5. Prevent self excitation resonance phenomenon that may occur in generators with long lines;
6. When using a small reactance grounding device for the neutral point of a reactor, a small reactor can also be used to compensate for the phase to phase and phase to ground capacitance of the circuit, in order to accelerate the automatic extinguishing of the secondary current and facilitate its use.
4、 Why is the percentage used to calculate the reactor
The current limiting reactor ensures that the closing inrush current does not exceed ten times the rated current of the capacitor, which can reduce the copper consumption and volume of the reactor. 4.5% -13% of reactors are used to suppress harmonics. If the network harmonics are large, such as 3rd, 5th, 7th, 11th, and high pass harmonics, only 13% of reactors can suppress harmonics above 3rd. If there are no 3rd harmonics, 6% of reactors can be used to cover harmonics above 5th, because the reactance required for harmonics above 5th is less than that of 5th harmonics.
Wuhan UHV specializes in the production of series resonance (also known as series resonance withstand voltage test device) and has been engaged in the electrical measurement industry for many years. Its products have first-class quality and welcome customers to come and purchase.