What is resonance? When the reactance of an inductor balances the reactance of a capacitor at a given frequency, resonance occurs. In this series resonant circuit (also known as series variable frequency resonant), the current will be maximum and the impedance will be minimum. In a parallel resonant circuit, the situation is exactly the opposite.
Resonance formula
The formula for resonance is:
2 * pi * f * L = 1 /(2 * pi * f * C)
Among them: 2 * pi=6.2832; F=frequency, measured in Hertz, L=inductance, measured in Henry, C=capacitance, measured in Farads
We will continue:
f = 1 / [2 * pi(sqrt LC)]
Among them: 2 * pi=6.2832; F=frequency, measured in Hertz, L=inductance, measured in Henry, C=capacitance, measured in Farads
A particularly simple radio frequency formula (please make sure you understand it) is:
LC = 25330.3 / f 2
Among them: f=frequency, measured in megahertz (Mhz), L=inductance, measured in microhenries (uH), C=capacitance, measured in picofarads (pF)
By using simple algebra, we can determine:
LC=25330.3/f2 and L=25330.3/f2 C and C=25330.3/f2 L
Resonant impedance
In a series resonant circuit, impedance is the lowest for the resonant frequency, while in a parallel resonant circuit, impedance is the highest for the resonant frequency. Refer to Figure 1.
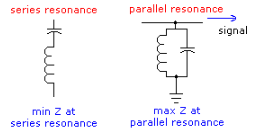
Figure 1- Resonance in Series and Parallel Circuits
For a series circuit in a resonant state, impedance increases continuously at frequencies away from resonance. For a parallel circuit in a resonant state, impedance decreases continuously at frequencies away from resonance.
A typical example is the large number of parallel circuits used in wireless communication. View the parallel resonant circuit above. During resonance, the circuit provides such a high impedance to the resonant circuit that it is almost invisible and the signal passes through. As the circuit deviates from its resonant frequency (up or down), it exhibits a decreasing impedance and gradually allows other signals to leak to ground. At frequencies far from resonance, parallel resonant circuits appear as short paths to ground. For series resonance, the opposite is true.




















